Unprocessing Images for Learned Raw Denoising
文章贡献有两点:
- Unprocess操作:转一个Clean图像到RAW。Process操作:逆Unprocess。
- 添加dataset-dependent noise 噪声,生成与真实噪图相同的噪图。
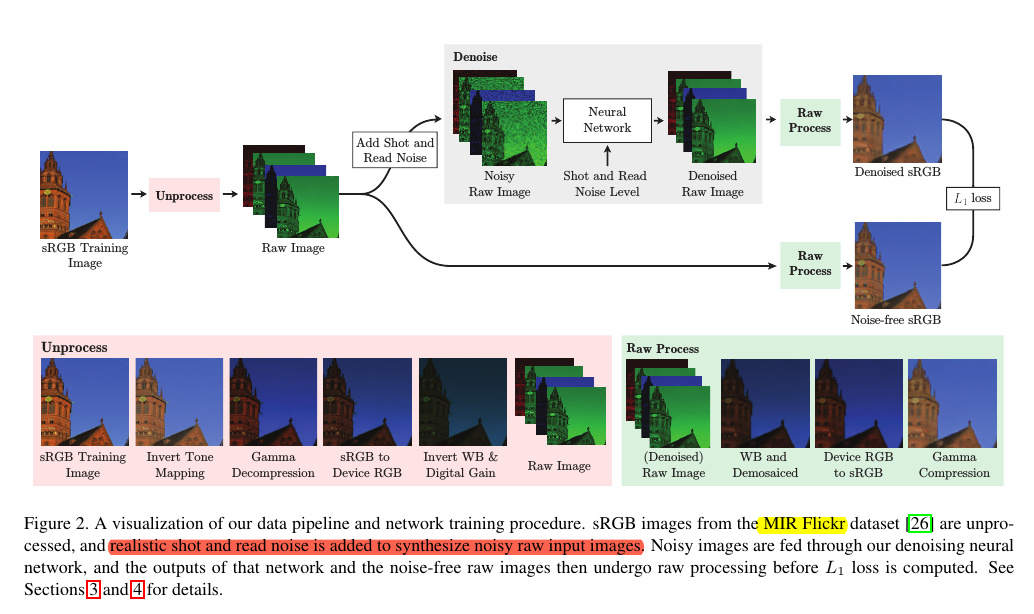
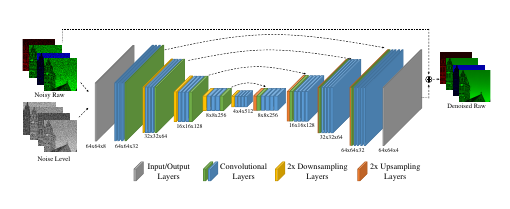
训练:
数据集:
- million images of the MIR Flickr extended dataset setting aside 5% of the dataset for validation and 5% for
testing - 将每一张来自Internet的数据集图像,这里使用的是来自MIR Flickr的图像。对其进行Unprocess,得到Raw Image,作者说该Unprocess pipeline是可逆的,可逆操作为Process。
- 在得到Raw Image后根据数据集的特征参数来添加shot and read噪声(Thus the values of λread and λshot can be calculated by the camera for a particular exposure and are usually stored as part of the metadata accompanying a raw image file.)。
在添加了噪声的RAW图像中进行去噪器的训练得到RAW的去噪结果,For both experiments, we minimize L1 loss between the output and ground-truth images.
- 针对SRGB模型,our “sRGB” model the network output and synthetic ground-truth are both transformed to sRGB space before computing the loss,
- 针对RAW模型, Our “Raw” model instead computes the loss directly between our network output and our raw synthetic ground-truth, without this processing. 直接RAW对应loss计算,不转为sRGB。
测试在DND上进行测试。
噪声,以及domain-aimed 噪声添加
RAW域的噪声分为两种噪声:1.是光子到达噪声,2.是sensor读取噪声。Sensor noise primarily comes from two sources: photon arrival statistics (“shot” noise) and imprecision in the readout circuitry (“read” noise)
两者结合,噪声图像可以看作:其中 $y$ 是观测后验。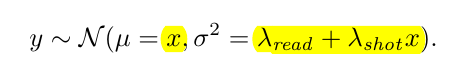
$\lambda{read} = g_d^2 \sigma_r^2$ , $\lambda{shot}=gd g_a$ 是由sensor’s 模拟,数字增益,以及固定读取方差 $\sigma_r^2$ 决定的。 $\lambda{read}$ $\lambda_{shot}$ 是可以通过相机的particular exposure and are usually stored as part of the metadata accompanying a raw image file.
作者计算了DND的所有 $log \lambda{read}$ $log\lambda{shot}$ ,下图蓝色所示,对其拟合得到红色线(加置信度)。
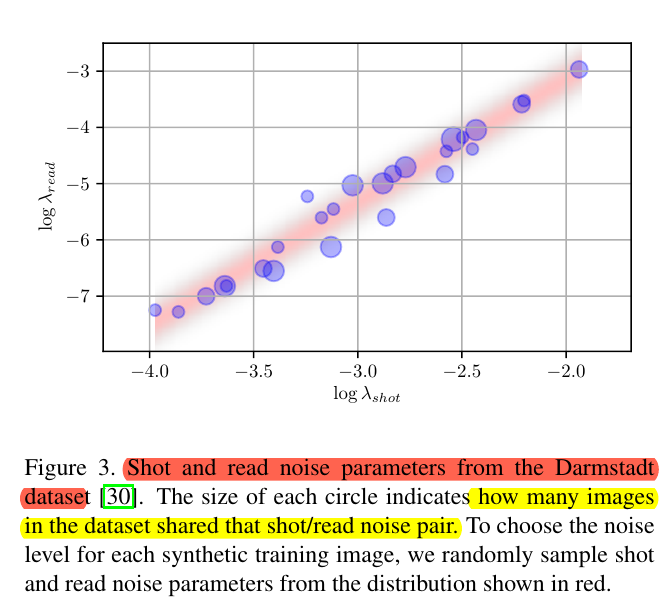

从其中抽样各个噪声,添加到RAW图中进行生成。
code of read and shot add->dataset
1 | def random_noise_levels(): |